Extracellular water analysis is an important testing procedure for testing the purity of water sources. This test can help identify and measure elements and compounds that may be present in a sample of extracellular fluid, including dissolved gases, suspended solids and ionic species of metals or minerals. With this procedure it is possible to accurately determine the quality of any water source, whether it is groundwater, rivers, lakes or even seawater.

Table Of Content:
- Interpreting Your Results - Inner Image
- Body Water: Percentage and Ratios You Should Know - InBody USA
- Understand extracellular water to keep your health in check
- InBody Test?
- Body Water: Percentages and Ratios You Should Know
- Extracellular Water to Total Body Water Ratio in Viral Liver Diseases ...
- Extracellular Water Ratio as an Indicator of the Development and ...
- The clinical application value of the extracellular-water-to-total-body ...
- Estimation of total body water and extracellular water with ...
- Extracellular water to total body water ratio predicts survival in ...
1. Interpreting Your Results - Inner Image
https://inner-image.com/resources/interpreting-your-results/
Oct 3, 2015 ... Extracellular Water/Total Body Water Analysis (ECW/TBW): ... Ratio of Extracellular Water to Total Body Water; an important indicator of body ...
2. Body Water: Percentage and Ratios You Should Know - InBody USA
https://inbodyusa.com/blogs/inbodyblog/40668865-your-body-and-you-a-guide-to-body-water/ Sep 19, 2019 ... Extracellular water is the water located outside your cells. The water in your blood falls into this category. Roughly 1/3 of your fluid is ...
Sep 19, 2019 ... Extracellular water is the water located outside your cells. The water in your blood falls into this category. Roughly 1/3 of your fluid is ...
3. Understand extracellular water to keep your health in check
https://www.phlabs.com/understand-extracellular-water-to-keep-your-health-in-check The best way to measure extracellular water is to divide your extracellular water by your total body water (ECW/TBW). The number you receive will represent the ...
The best way to measure extracellular water is to divide your extracellular water by your total body water (ECW/TBW). The number you receive will represent the ...
4. InBody Test?
http://qr.inbody.com/ri/570/adult/en-US
ECW/TBW, the ratio of Extracellular Water to Total Body Water, is an important indicator of body water balance. In a healthy state, ECW Ratio should be between ...
5. Body Water: Percentages and Ratios You Should Know
https://aquavitality.com/body-water-percentage/ Extracellular water is the water located outside your cells. The water in your blood falls into this category. Roughly 1/3 of your fluid is attributed to ECW, ...
Extracellular water is the water located outside your cells. The water in your blood falls into this category. Roughly 1/3 of your fluid is attributed to ECW, ...
6. Extracellular Water to Total Body Water Ratio in Viral Liver Diseases ...
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6115798/
Aug 12, 2018 ... Multivariate analysis showed that age, prothrombin time, serum albumin, and alanine aminotransferase were significant factors linked to ECW/TBW ...
7. Extracellular Water Ratio as an Indicator of the Development and ...
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33185511/ Nov 13, 2020 ... Extracellular Water Ratio as an Indicator of the Development and Severity of Leg Lymphedema Using Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis · Authors.
Nov 13, 2020 ... Extracellular Water Ratio as an Indicator of the Development and Severity of Leg Lymphedema Using Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis · Authors.
8. The clinical application value of the extracellular-water-to-total-body ...
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0899900721004299 Body-composition analysis using bioelectrical impedance analysis is gradually becoming more widely used in clinical practice. The ratio of extracellular water ( ...
Body-composition analysis using bioelectrical impedance analysis is gradually becoming more widely used in clinical practice. The ratio of extracellular water ( ...
9. Estimation of total body water and extracellular water with ...
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25886709/ Abstract. Purpose: Bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA) equations can predict total body water (TBW) and extracellular water (ECW) in non-athletic ...
Abstract. Purpose: Bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA) equations can predict total body water (TBW) and extracellular water (ECW) in non-athletic ...
10. Extracellular water to total body water ratio predicts survival in ...
https://nutritionandmetabolism.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12986-022-00667-3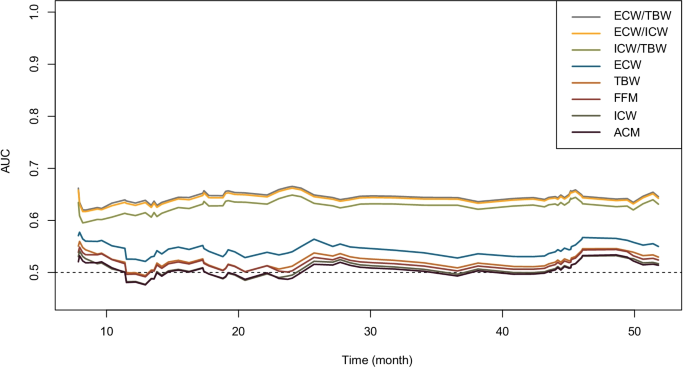 May 7, 2022 ... Body water measured by bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA) predicts the outcomes of many diseases. This study aimed to evaluate the ...
May 7, 2022 ... Body water measured by bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA) predicts the outcomes of many diseases. This study aimed to evaluate the ...
Q1: What is Extracellular Water Analysis?
Extracellular water analysis is a testing procedure used to identify and measure elements and compounds that may be present in a sample of extracellular fluid, such as dissolved gases, suspended solids and ionic species of metals or minerals.
How does Extracellular Water Analysis work?
The process involves taking a sample of extracellular fluid into a laboratory environment where specialized equipment can detect the presence of various contaminants or pollutants. Each element or compound present in the sample will be measured according to its chemical properties, allowing for accurate results.
When should Extracellular Water Analysis be done?
Extracellular water analysis should be conducted whenever there is concern about contamination levels in a given water source – like drinking water sources like wells – as well as aquatic environments such as lakes or ponds. In addition, this type of test can also provide valuable data when monitoring natural resources used for recreation purposes such as fishing and boating.
What are some benefits associated with conducting an Extracellular Water Analysis?
By conducting this type of test you are able to identify potential problems with your water source before they affect your health or the environment around you. In addition, by understanding what’s present in your water supply you can make better decisions regarding how best to protect it from pollution or contamination from outside sources.
Are there any limitations associated with performing an Extracellular Water Analysis?
While one benefit to this type of testing is its accuracy when measuring pollutants – especially those below permissible limits – its limitations lie mainly in its cost due to having access to specialised equipment which may not always be easily available or affordable for smaller-scale operations.
Conclusion:
Overall, performing an extracelluar water analysis helps ensure that our waters are safe by measuring certain elements and compounds that would otherwise not be detectable without specialized tools. By conducting regular checks we can keep our natural resources clean and protected from potential threats posed by man-made contaminants.
